Advantages of zinc
Zinc has many advantages, here are the main ones:
- Better precision
- Lifetime tool guarantee
- Superior tensile strength and elongation
- Narrower and longer core holes
- Thin wall sections are possible
- Smaller release angles
- Superior impact strength
- Easier to machine
- Better formability
- Faster shot speed – lower production cost
- Superior pressure tightness
- no need for impregnation
- More machining options
- Material does not generate sparks
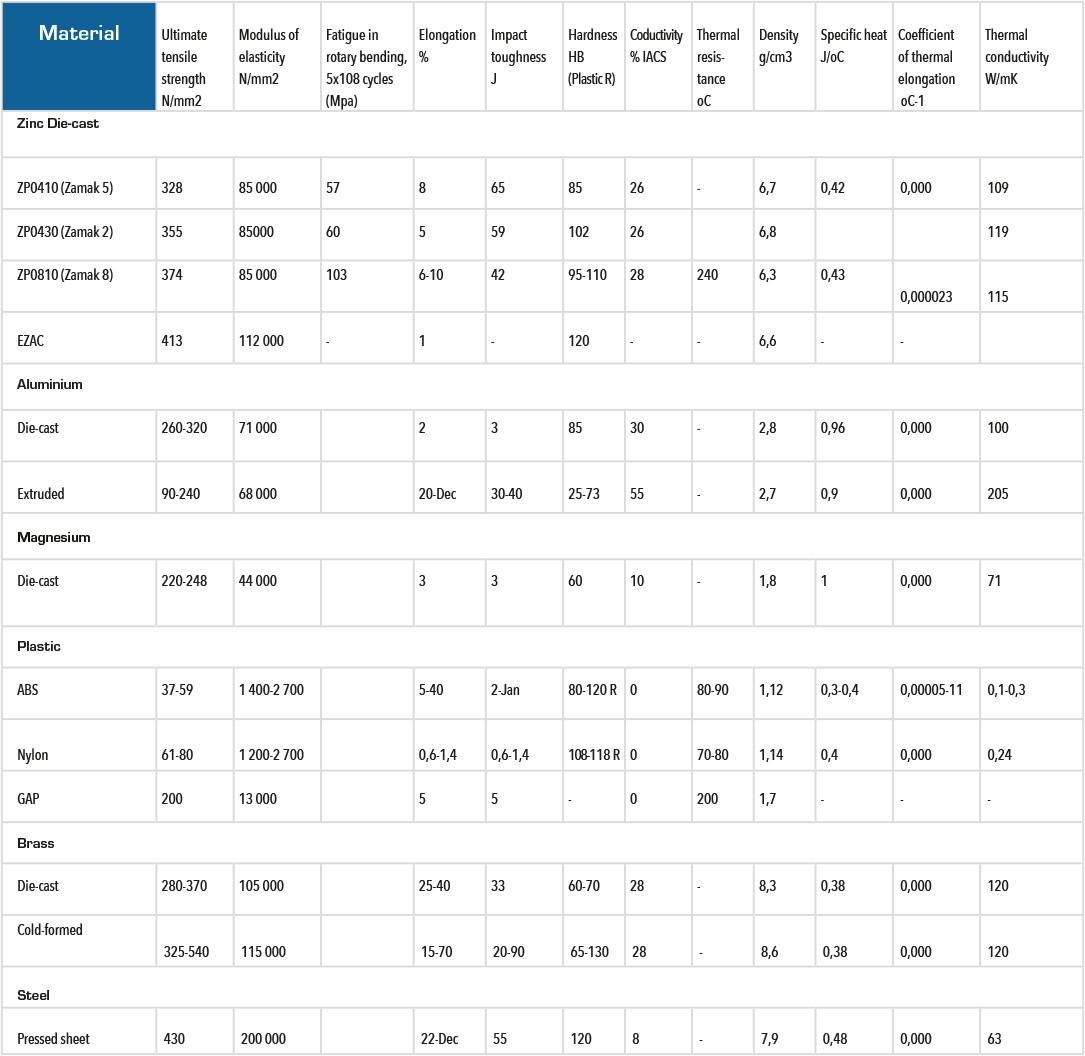

Zinc versus aluminium
Die casting is a method that is used in the manufacture of both zinc and aluminium parts. The main difference between the two are their weight and melting point. Aluminium is lighter than zinc, but zinc has a lower melting point. This means that manufacturing with zinc is quicker, more energy-efficient and has lower production costs. Zinc is therefore the best choice for slightly smaller products, where the weight is less important. Another important difference is that casting precision is significantly better and the strength of zinc is considerably higher, so wall thickness can be reduced. Wall thicknesses down to 0.4 mm are achievable. We give a lifetime guarantee on our tools, while tools for aluminium often have a maximum lifetime of 100,000 shots.
Zinc versus plastic
Injection moulding of plastic and die casting of zinc are relatively similar as manufacturing methods. But the materials themselves differ considerably from each other. With zinc you get higher strength. The metallic properties of zinc also give it a number of advantages. The electronics industry, for example, often uses zinc because it provides an effective screen against electromagnetic radiation. Products made from zinc generally have a longer life and can cope with rougher handling. The environmental aspect is also important. Plastic is not biodegradable, while zinc is 100 per cent recyclable.


Zinc versus machined products
If a product is to be produced in low volume its shape can be machined out of a blank. This is a method that is used when the cost of making a casting tool is too high in relation to the volume. Die casting of zinc is even competitive for smaller volumes, but the larger the volume that is required, the more likely it is that die-cast zinc will be a more cost-effective choice.
Zinc versus brass
Brass can also be cast. However, it is an expensive material and often requires machining afterwards, while zinc can be die-cast in finished form. Brass should therefore only be used when the specific properties of brass are required. It has very good thermal conductivity, for example. But if it is simply an intricate shape that is required, then zinc is superior.


Zinc versus sheet metal
Products that are made from sheet metal can often be replaced with die-cast zinc. It is possible to cast zinc with very thin walls that give the final product low weight. While a sheet metal product requires stamping, bending and cutting, zinc can be cast in a single piece. This also makes the manufacturing process more efficient and often results in a lower cost for the customer.









